Soil Carbon
Click here to view our Soil Carbon Protocol Version 3.0
A summary of the changes from Version 2.0 to Version 3.0 can be found here: Soil Carbon Update Summary
Soil Protocol Updates
February 2026
June 2021
October 2022
The top 30 centimeters of the world’s soils contain nearly twice the carbon of Earth’s atmosphere.
Sustaining and restoring soils can mitigate GHG emissions through enhanced carbon sequestration. These practices have the added benefit of promoting habitat conservation, sustainable food production, and flood resilience. BCarbon’s Soil Carbon Protocol provides a measurement-based approach to quantifying and crediting increases in soil organic carbon while safeguarding soil’s other essential functions.
Read our Protocol here.
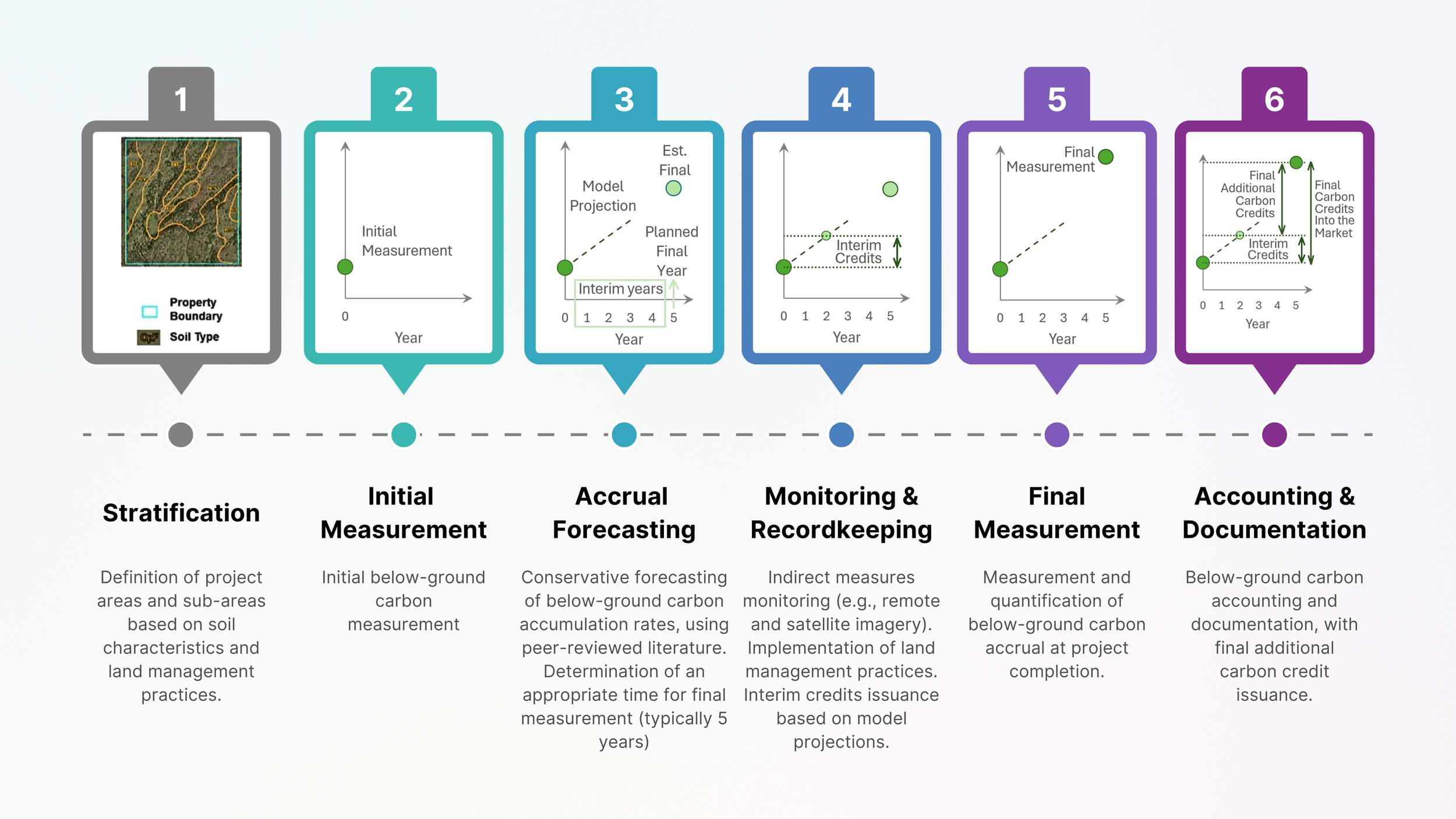
This document defines methods for quantifying the increase in soil organic carbon achieved over time on a property with the necessary statistical reliability to support the issuance and sale of carbon credits. The 6-step process, addressing site selection and stratification, quantification of the accrued carbon mass, and interim credit estimates, is summarized in the graphic below. Equivalent methods not included in this standard may be applied subject to approval by BCarbon.
For applicants wishing to conduct a combined soil & forest carbon project, start by reviewing our Soil & Forest Guidance.
Have questions?
Click here to access our Soil Carbon Protocol FAQ. Or, email us at info@bcarbon.org
Apply:
Submit a Letter Of Intent
Submit a Soil Carbon Application Checklist
Thanks to GSI Environmental Inc. and the BCarbon Soil Metrics Subcommittee for their support in the development of this Protocol.